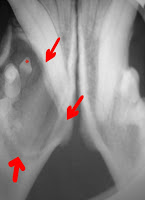
Dentigerous cysts:
-
What are dentigerous cysts?
- A closed sac of serous fluid surrounding an impacted or partially erupted tooth.
-
What causes dentigerous cysts?
- When a tooth does not erupt normally, the pressure it puts on the dental follicle causes accumulation of fluid between the enamel epithelium and the crown.
-
Can cysts appear impacted for other reasons?
- Cysts can originate from developing teeth that are erupting normally
- Cysts can form at the root of a tooth that has been injured by trauma or cavities
- Cysts can be oral masses that are neoplastic in origin e.g. calcifying odontogenic cyst
-
What effect do dentigerous cysts have?
- Due to the tendency for dentigerous cysts to expand rapidly, they may cause pathological fractures of jaw bones.
-
How is it diagnosed?
- Step 1: count the teeth; unerupted teeth can be diagnosed around 7 months of age; look for soft fluid swellings of the gums where a tooth should be present
- Step 2: take dental radiographs
- Step 3: histopathology should be performed if a tooth is not found within the cyst
-
How is it treated or prevented?
- Extract impacted tooth before a cyst forms
- Completely remove the soft tissue lining of a cyst
- Extract neighboring teeth that have suffered severe bone loss
- Bone grafting may be indicated in patients at risk for jaw fractures
COMING SOON: Gingival Hyperplasia